Oct 3, 2016
Basic Brain Biology
Your brain is made of cells. Those cells are called neurons. Neurons transmit signals in the form of electricity (aka .positive and negative charges). One end of a neuron will build a signal or charge, and once it reaches a certain threshold, then a signal is send down the axons.
Most of the cells in your body touch and transmit signals and pass chemicals through their membranes. Neurons do not touch. The terminals of one will get really really close to the dendrites of another.
They're really good at the telephone game - mostly because the body tries to minimize the number of neurons involved in passing a signal.
Axons are coated in myelin. Myelin insulates the axon that helps the signal being sent travel faster, and prevents it from getting lost to something else touching it. You want the signal to have to same strength when it reaches its destination as it did when it left its source.
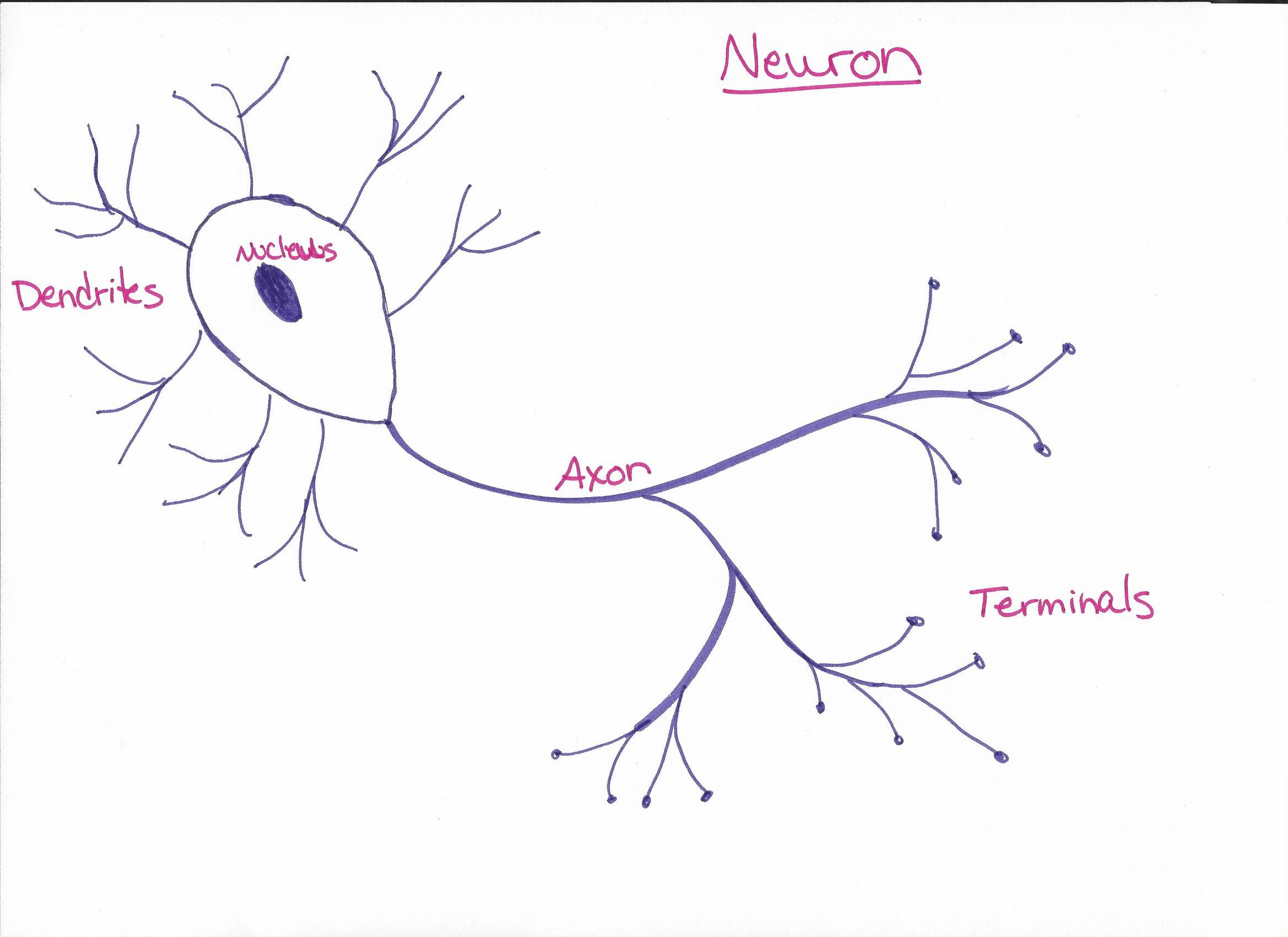
Parts of a neuron
Dendrites: receives signals from previous neuron
Cell body: contains the nucleus and creates and translates
signals
Axon: the "wire" that transmits signals
Terminals: sends signals to the next neuron
Grey matter - cell bodies,
dendrites, and terminals
White matter -
axons wrapped in myelin
Grey matter - information storage
and translation
White matter -
information transmission
Brain: grey matter is on the outside, white matter is
on the inside
Spinal cord: grey matter is on the inside, white matter is on
the outside.
PS. Grey? Gray? IDK!!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/

